ref ) 항공안전법 시행규칙
제181조(계기비행방식 등에 의한 비행ㆍ접근ㆍ착륙 및 이륙)
⑥ 계기착륙시설(Instrument Landing System/ILS)은 다음 각 호와 같이 구성되어야 한다.
1. 계기착륙시설은 방위각제공시설(LLZ), 활공각제공시설(GP), 외측마커(Outer Marker), 중간마커(Middle Marker) 및 내측마커(Inner Marker)로 구성되어야 한다.
2. 제1종 정밀접근(CAT-I) 계기착륙시설의 경우에는 내측마커를 설치하지 아니할 수 있다.
3. 외측마커 및 중간마커는 거리측정시설(DME)로 대체할 수 있다.
4. 제2종 및 제3종 정밀접근(CAT-Ⅱ 및 Ⅲ) 계기착륙시설로서 내측마커를 설치하지 아니하려는 경우에는 항행안전시설 설치허가 신청서에 필요한 사유를 적어야 한다.
ref ) AIM
1-1-9 Instrument Landing System (ILS)
- General
- The ILS is designed to provide an approach path for exact alignment and descent of an aircraft on final approach to a runway.
- The basic components of an ILS are the localizer, glide slope, and Outer Marker (OM) and, when installed for use with Category II or Category III instrument approach procedures, an Inner Marker (IM).
- The system may be divided functionally into three parts:
- Guidance information: localizer, glide slope.
- Range information: marker beacon, DME.
- Visual information: approach lights, touchdown and centerline lights, runway lights.
- The following means may be used to substitute for the OM:
- Compass locator; or
- Precision Approach Radar (PAR); or
- Airport Surveillance Radar (ASR); or
- Distance Measuring Equipment (DME), Very High Frequency Omni-directional Range (VOR), or Nondirectional beacon fixes authorized in the Standard Instrument Approach Procedure; or
- Very High Frequency Omni-directional Radio Range (VOR); or
- Nondirectional beacon fixes authorized in the Standard Instrument Approach Procedure; or
- A suitable RNAV system with Global Positioning System (GPS), capable of fix identification on a Standard Instrument Approach Procedure.
- Where a complete ILS system is installed on each end of a runway; (i.e., the approach end of Runway 4 and the approach end of Runway 22) the ILS systems are not in service simultaneously.
- Localizer
- The localizer transmitter operates on one of 40 ILS channels within the frequency range of 108.10 to 111.95 MHz. Signals provide the pilot with course guidance to the runway centerline.
- The approach course of the localizer is called the front course and is used with other functional parts, e.g., glide slope, marker beacons, etc. The localizer signal is transmitted at the far end of the runway. It is adjusted for a course width of (full scale fly-left to a full scale fly-right) of 700 feet at the runway threshold.
- The course line along the extended centerline of a runway, in the opposite direction to the front course is called the back course.
-
CAUTION-
Unless the aircraft's ILS equipment includes reverse sensing capability, when flying inbound on the back course it is necessary to steer the aircraft in the direction opposite the needle deflection when making corrections from off-course to on-course. This “flying away from the needle” is also required when flying outbound on the front course of the localizer. Do not use back course signals for approach unless a back course approach procedure is published for that particular runway and the approach is authorized by ATC.
- Identification is in International Morse Code and consists of a three-letter identifier preceded by the letter I (●●) transmitted on the localizer frequency.
EXAMPLE-
I-DIA
- The localizer provides course guidance throughout the descent path to the runway threshold from a distance of 18 NM from the antenna between an altitude of 1,000 feet above the highest terrain along the course line and 4,500 feet above the elevation of the antenna site. Proper off-course indications are provided throughout the following angular areas of the operational service volume:
- To 10 degrees either side of the course along a radius of 18 NM from the antenna; and
- From 10 to 35 degrees either side of the course along a radius of 10 NM. (See FIG 1-1-6.)
FIG 1-1-6
Limits of Localizer Coverage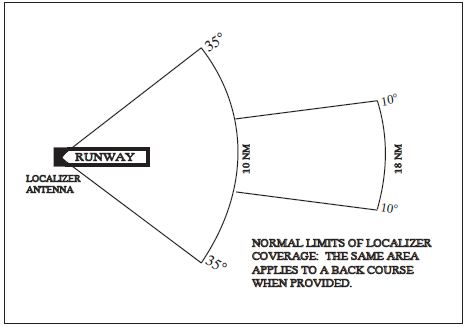
- Unreliable signals may be received outside of these areas. ATC may clear aircraft on procedures beyond the service volume when the controller initiates the action or when the pilot requests, and radar monitoring is provided.
- The areas described in paragraph 1-1-9 b5 and depicted in FIG 1-1-6 represent a Standard Service Volume (SSV) localizer. All charted procedures with localizer coverage beyond the 18 NM SSV have been through the approval process for Expanded Service Volume (ESV), and have been validated by flight inspection. (See FIG 1-1-7.)
'Aviation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ECON speed, 경제속도 -정리중 (0) | 2024.03.17 |
|---|---|
| ATIS (0) | 2024.03.17 |
| RAIM-ㅈㄹㅈ (0) | 2024.03.17 |
| 착륙거리 - 뇌절 (3) | 2024.03.17 |
| 속도조절 - 뇌절중 (1) | 2024.03.17 |